Contributors:
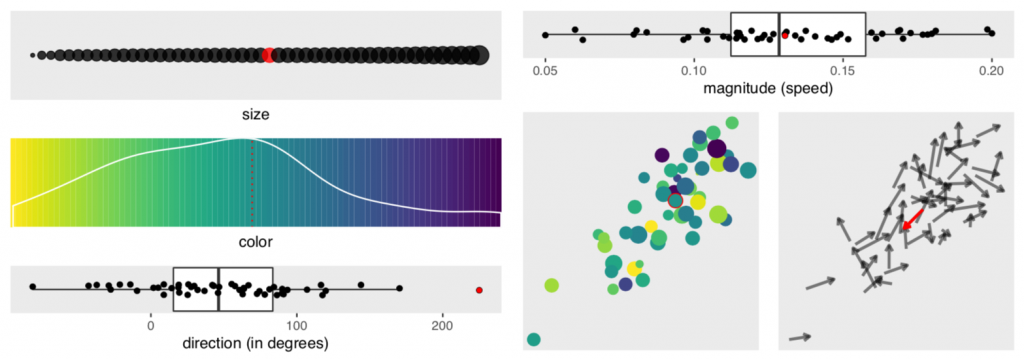
We report the results of a crowdsourced experiment that measured the accuracy of motion outlier detection in multivariate, animated scatterplots. The targets were outliers either in speed or direction of motion and were presented with varying levels of saliency in dimensions that are irrelevant to the task of motion outlier detection (e.g., colour, size, position). We found that participants had trouble finding the outlier when it lacked irrelevant salient features and that visual channels contribute unevenly to the odds of an outlier being correctly detected. Direction of motion contributes the most to the accurate detection of speed outliers, and position contributes the most to accurate detection of direction outliers. We introduce the concept of saliency deficit in which item importance in the data space is not reflected in the visualization due to a lack of saliency. We conclude that motion outlier detection is not well supported in multivariate animated scatterplots.
![]() This research was given an honourable mention at CHI 2019.
This research was given an honourable mention at CHI 2019.
Materials used to conduct this research are available for download here.
Publications
-
[pods name="publication" id="4212" template="Publication Template (list item)" shortcodes=1]